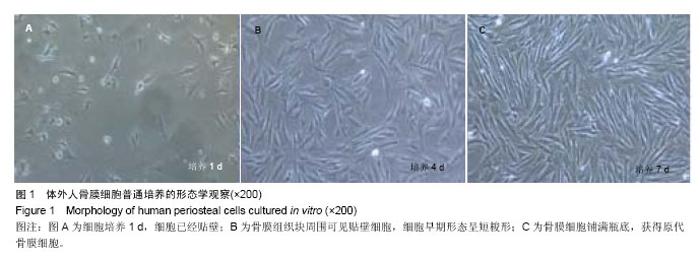
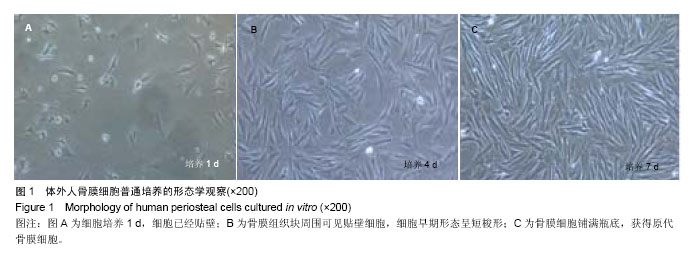
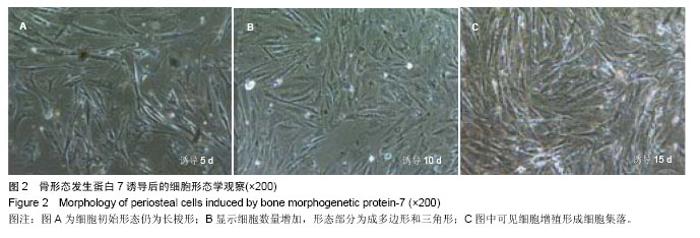
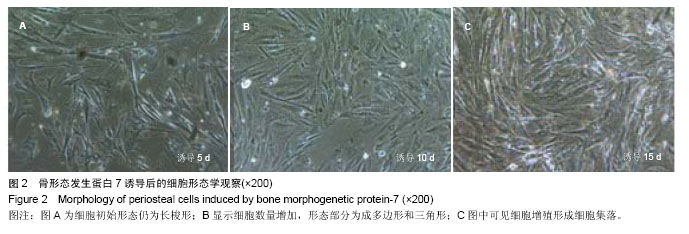
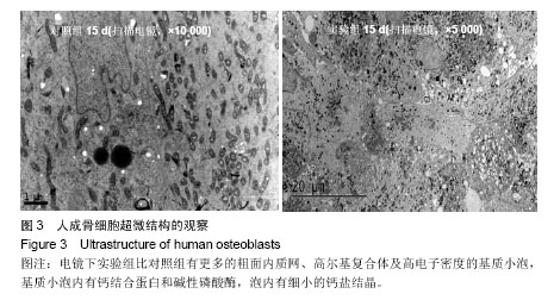
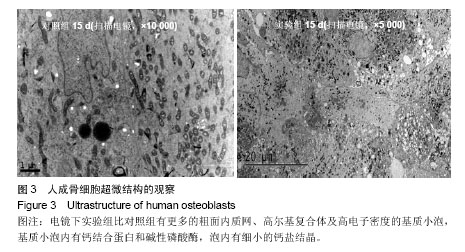
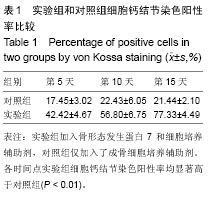
| [1]Jang YS, Choi CH, Cho YB, et al. Recombinant human BMP-2 enhances osteogenesis of demineralized bone matrix in experimental mastoid obliteration.Acta Otolaryngol. 2014; 20:1-6.
[2]Fabender M,Minkwitz S,Strobel C,et al.Stimulation of bone healing by sustained bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) delivery.Int J Mol Sci.2014;15(5):8539-8552.
[3]Wozney JM. The bone morphogenetic protein family : multifunctional cellular regulators in the embryo and adult.Eur J Oral Sci.1998;106(Suppl1):160-166.
[4]Moon JS, Kim SH, Oh SH, et al.Relaxin Augments BMP-2-Induced Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(7):1586-1596.
[5]Hu JJ, Liu YW, He MY, et al.Proteomic analysis on effectors involved in BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation of beagle bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Proteome Sci. 2014;12(1):13
[6]Zhao HB, Qi SN, Dong JZ,et.al. Salidroside induces neuronal differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells through Notch and BMP signaling pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014;71C:60-67.
[7]Hughes FJ, Collyer J, Stanfield M,et al. The effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2, -4, and-6 on differentiation of rat osteoblast cells in vitro. Endocrinology. 1995;136:2671-2677.
[8]Lecanda F, Avioli LV, Cheng SL. Regulation of bone matrix protein expression and induction of differentiation of human osteoblasts and human bone marrow stromal cells by bone morphogenetic protein-2.J Cell Biochem.1997;67:386-398.
[9]Yamaguchi A, Ishizuya T, Kintou N, et al. Effects of BMP-2, BMP-4, and BMP-6 on osteoblastic differentiation of bone marrow-derived stromal cell lines, ST2 and MC3T3-G2/PA6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996;220:366-71.
[10]Wang J, Guo J, Liu J, at al.BMP-functionalised coatings to promote osteogenesis for orthopaedic implants.Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(6):10150-68.
[11]胡丽玲,李晓霞,张镜宇,等.BMP2与BMP7嵌合表达产物可诱导成骨细胞分化[J].天津医药,2009,10(37):820-822
[12]温学红,郭若霖,程瑞芳,等.BMP-2和地塞米松对成人成骨细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].临床检验杂志,2005,2(3):34-37.
[13]Bei K, Du Z, Xiong Y, et al. BMP7 can promote osteogenic differentiation of human periosteal cells in vitro. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(9):8845-8851.
[14]轩昆,杨富生,文玲英,等.BMP3、BMP4、BMP7在犬牙根发育过程中的表达研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2006,22(6):807-810.
[15]祝联,陈付国,刘伟,等.骨髓基质干细胞转染腺病毒BMP7后的成骨改变[J].中华整形外科杂志,2006,22(3):59-62.
[16]郭晓莹,朱文俊,宋祥晨,等. BMP-7在牙龈蛋白酶诱导成骨细胞凋亡中的保护作用.中华老年口腔医学杂志.2013,11(3):140-144.
[17]康健,侯洋,周许辉,等. TGF-3和BMP-7腺病毒共转染兔骨髓间充干细胞向类髓核细胞分化的研究,中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014, 24(2):157-163
[18]Chaudhary LR, Hofmeister AM, Hruska KA. Hruska Differential growth factor control of bone formation through osteoprogenitor differentiation. Bone. 2004;34(3):402-411.
[19]Chen TL, Shen WJ, Kraemer FB.Kraemer Human BMP-7/OP-1 Induces the Growth and Differentiation of Adipocytes and Osteoblasts in Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Cultures.J Cell Biochem. 2001;82(2):187-99.
[20]Zhu L, Chuanchang D, Wei L, et al.Enhanced healing of goat femur-defect using BMP7 gene-modified BMSCs and load-bearing tissue-engineered bone.J Orthop Res. 2010; 28(3): 12-418.
[21]宋守礼,朱盛修,张伯勋,等.经皮注射自体骨膜细胞修复骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1997,17(11):696-698.
[22]Akihiko T, Yukie K, Kiyonori H, et al. Osteogeneic potential of cultured periosteal cells in distracted bone gap in rabbits.J Sur Res.1998;78(1):68-77.
[23]贝抗胜,刘建平,吴强,等.人骨膜细胞体外培养的实验研究与临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(17):1329-1331. |